Today, more than 80% of global energy needs are coming from fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gases. Due to the global population growth, the energy demand is increasing by the day. Researches show that the ever-growing consumption of fossil fuels may lead to a potential energy crisis in another five or six decades. Apart from the fast-decreasing fossil reserves, its impact on the global climate has shifted the attention of the world towards more sustainable energy solutions. Among those, microbial energy conversion shows a very promising future in this field.

Microbes can be found in almost every place of the planet Earth. Among them some of the microorganisms have the ability to convert chemical energy into biofuels and some of them are capable of breaking down the organic matter to produce electricity. These biofuels include hydrogen, methane, and ethanol. Bioethanol is one of the most common types of biofuels manufactured from microbial fermentation of crop sources. Using Bioethanol has an advantage over fossil fuels because of its renewability and the fact that it can be produced by using many different substrates by using different types of microorganisms. Methane and hydrogen are also used as fuels that can be produced using microorganisms. The microbial fuel cell (MFC) is used to generate electricity directly by breaking down organic material using microbes as a catalyst. These devices are capable of converting chemical energy contained in substrates into electrical energy. The MFC works in a similar way like batteries. It consists of an anode chamber and cathode chamber which are separated by a proton exchange membrane. In an anode chamber, organic materials are degraded and produce electrons and protons using microbes as the catalyst. These electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through the external circuit while the protons go through the proton exchange membrane to the cathode and forming water by reacting with oxygen thus creating a usable form of energy.
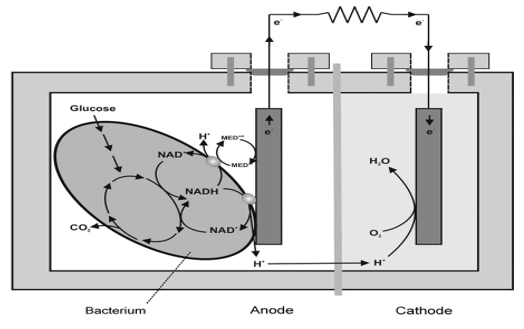
Most of the microbial energy conversion techniques are still not developed enough to be properly applied in the energy industry. But with proper research and implementations, it could be used to fulfill our ever-growing energy demands while creating a sustainable environment.
Image credits:
- Post, T. J. (2018, August 15). Corruption allows mine-mouth coal plants to pollute. The Jakarta Post. https://www.thejakartapost.com/academia/2018/08/15/corruption-allows-mine-mouth-coal-plants-to-pollute.html
- Aelterman, P., Rabaey, K., Clauwaert, P., & Verstraete, W. (2006). Microbial fuel cells for wastewater treatment. Water Science and Technology, 54(8), 9–15. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2006.702
References
- Microbial Energy Conversion: This report is based on a colloquium, sponsored by the American Academy of Microbiology, convened March 10-12, 2006, in San Francisco, California. Washington (DC): American Society for Microbiology; 2006. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563531/ doi: 10.1128/AAMCol.10Mar.2006